Appearance
文件上传
- 二进制传输:用二进制流的形式传输文件
- base64:把文件转为base64字符串传输
文件相关的js对象解析
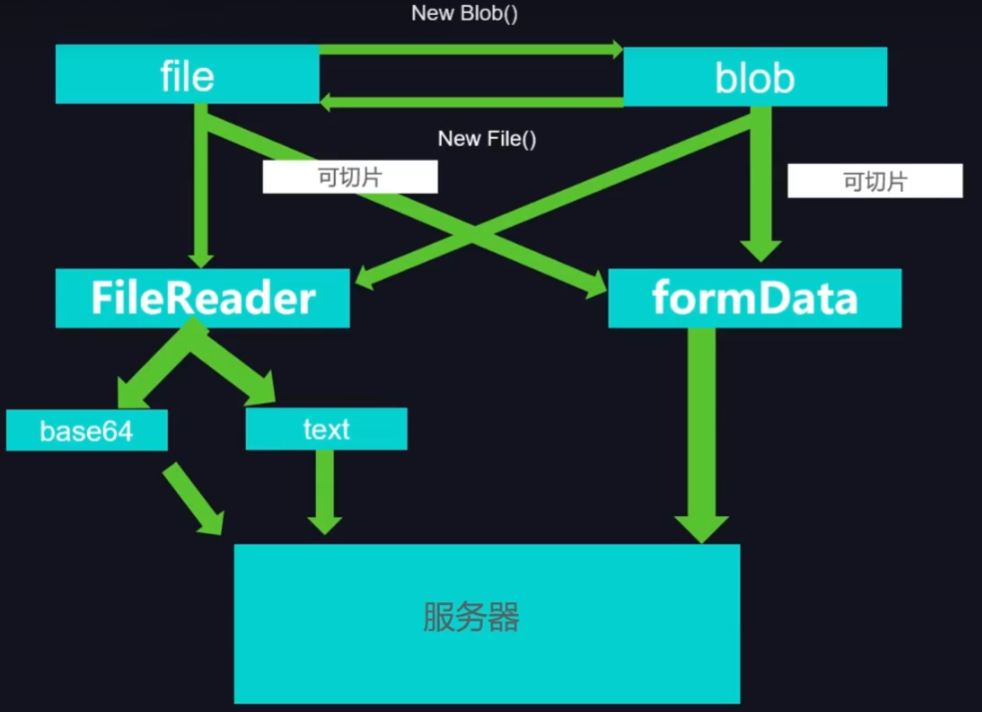
Blob对象: 把文件转换成二进制形式获取为blob对象file: 通过input标签读取过来的对象(二进制)formData: 可以用来搭载blob对象来传输fileReader: 多用于把文件读取为某种形式,如文本,base64
TIP
file 是 Blob对象的子类 本质上还是 Blob
使用formData
vue
<script setup lang="ts">
import axios from 'axios'
function onFileChange(e: any) {
console.log(e.target.files);
const file = e.target.files[0];
// 判断文件大小不能超过10KB
if (file.size > 10000) {
alert('文件大小不能超过10KB');
console.log(e);
console.log(e.target.value);
e.target.value = ''
return
}
// 限制文件后缀
let ext = file.name.split('.').pop();
console.log(ext);
if (ext !== 'xls' && ext !== 'jpeg' && ext !== 'gif') {
alert('只能上传xls、jpeg、gif格式的文件');
e.target.value = ''
return
}
console.log('file', file);
// 新建formDate对象
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', file)
formData.append('aaa', 'aaa')
console.log(formData);
const url = 'http://localhost:8080/upload'
axios.post(url, formData)
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<input type="file" @change="onFileChange">
</div>
</template>
<style scoped></style>转成base64
ts
// 新建fileReader对象
let reader = new FileReader();
let base64 = reader.readAsDataURL(file);
reader.onload = function () {
console.log(reader.result); // base64
imgUrl.value = reader.result as string
}
console.log(base64); // undefined多文件上传
ts
const imgList = ref<Array<any>>([])
const base64List = ref<Array<any>>([])
// 多文件上传
function onFileChange2(e: any) {
const fileList= e.target.files
console.log(e.target.files);
for (let i = 0; i < fileList.length; i++) {
imgList.value.push(fileList[i])
let reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsDataURL(fileList[i]);
reader.onload= function (){
base64List.value.push(reader.result)
}
}
}大文件切片
ts
async function f3(e:any){
let file = e.target.files[0] as File
// slice是Blob对象的方法,但是file对象是Blob对象的子类
// 大文件切片
let current = 0
let size = 50000
let fileSize = file.size
while(current<fileSize){
let _sli = file.slice(current,current+size)
const form = new FormData()
form.append(file.name,_sli)
form.append('partSize',current+size+'')
await axios.post('http://localhost:3000/file',form)
current += size
}
// 切图片
// const partUrl = ref()
// let _sli = file.slice(0,10000)
// console.log(_sli);
// 转成base64
// const fr = new FileReader
// fr.readAsDataURL(_sli)
// fr.onload = function(){
// partUrl.value = fr.result as string
// }
}使用了 async 关键字标识它是一个异步函数,并在 axios.post 方法前使用了 await 关键字。 这样做的好处是,await 会暂停函数的执行,直到 axios.post 返回一个结果(即请求完成)后才会继续执行循环的下一次迭代。 这样确保了文件块的发送是按照正确的顺序进行的,不会同时发起多个请求。
断点续传
在localStorage中存储该上传文件的已经传输大小
ts
async function f3(e: any) {
let file = e.target.files[0] as File
// slice是Blob对象的方法,但是file对象是Blob对象的子类
// 大文件切片
let current = 0
let size = 50000
let fileSize = file.size
let localPercent = localStorage.getItem(file.name)
if (localPercent) {
current = Number(localPercent)
}
while (current < fileSize) {
let _sli = file.slice(current, current + size)
const form = new FormData()
form.append(file.name, _sli)
form.append('partSize', current + size + '')
await axios.post('http://localhost:3000/file', form)
current += size
localStorage.setItem(file.name, current + '')
percent.value = Math.min((current / fileSize) * 100, 100)
}
}关系: