Appearance
组件通信
父向子传参
- 父组件传递数据 子组件标签身上绑定属性
- 子组件接收数据,props的参数
jsx
function Son(props){
// props 对象里面包含了父组件传递过来的所有的数据
return <div>this is son,{props.name}</div>
}
function Son({name}){
// 也可以这么写,直接解构出来
return <div>this is son,{name}</div>
}
function App(){
const name = 'this is app name'
return(
<>
<Son name={name} />
</>
)
}props说明
props可传递任意的数据- 数字、字符串、布尔值、对象、数组、函数、JSX
props是只读对象- 子组件只能读取
props中的数据,不能直接进行修改,父组件的数据只能父组件修改
- 子组件只能读取
- 特殊的prop children
- 当我们把内容嵌套在子组件标签中时,父组件会自动在名为 children 的 prop 属性中接收该内容(虚拟DOM)
jsx<Son> <span>这是span</span> </Son>
子向父传参
在子组件中调用父组件的函数
jsx
function Son(props) {
console.log(props);
const [count,setCount] = useState(0)
return (
<>
<span>{count}</span>
<button onClick={()=>setCount(count+1)}>+1</button>
<button onClick={()=>props.getMsg(count)}>发送子组件数据</button>
</>
)
}
function App() {
function getMsg(msg) {
console.log('父组件拿到数据了', msg)
}
return (
<div>
this is App
<Son getMsg={getMsg} />
</div>
)
}兄弟组件进行通讯
使用状态提升实现兄弟组件通信(利用共同的父组件来传参,先子传父,再父传子)
跨层级组件通信
使用context机制跨层级组件通信 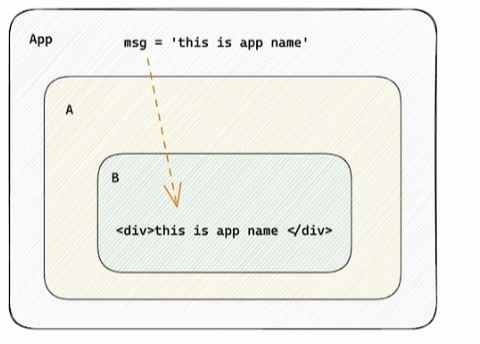 实现步骤:
实现步骤:
- 使用
createContext方法创建一个上下文对象 Ctx - 在顶层组件 (App) 中通过
Ctx.provider组件提供数据 - 在底层组件 (B) 中通过
useContext钩子函数获取消费数据
jsx
const ctx = createContext()
function App() {
const msg = 'App msg'
return (
<ctx.Provider value={msg}>
<A />
</ctx.Provider>
)
}
function B() {
const msg = useContext(ctx)
return (
<>
<h1>BBB,{msg}</h1>
</>
)
}
function A() {
return <B />
}